. . WOMEN’S EQUALITY . .
An article by Isabelle Grégoire from the International Development Research Centre (reprinted as non-commercial use)
After the 1994 genocide, 70% of Rwanda’s population was made up of women who had become heads of household. An unprecedented demographic situation that has led this formerly patriarchal country down the path of gender equality. Today, the government even promotes positive masculinity.
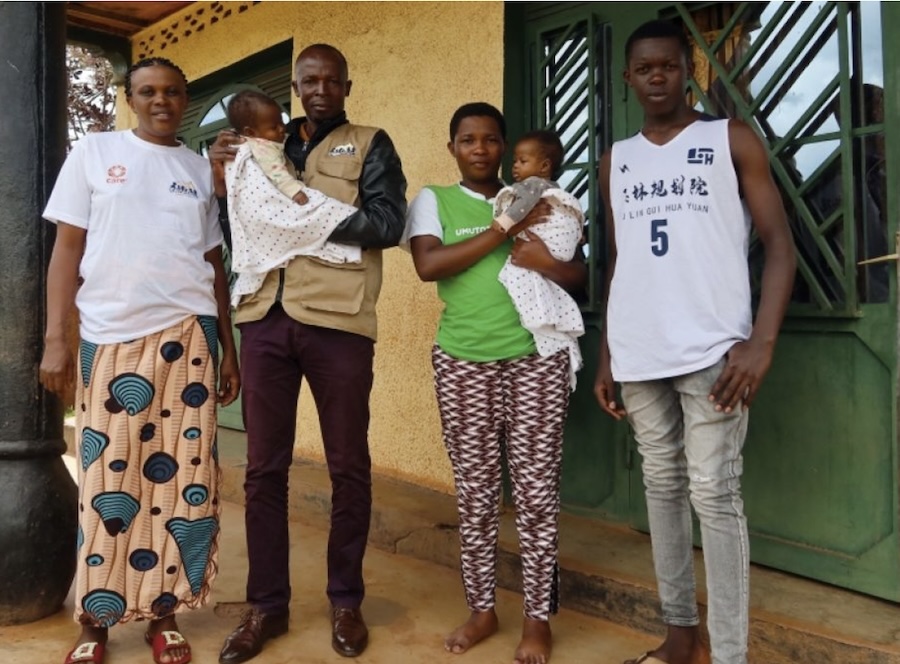
Thanks to the BAHO workshops, Théoneste Nyakabaji has gone from being an absent father to his earlier children to being a committed father to his two twin daughters. He is pictured with his wife, Claudine Umugwaneza (left) and four of their children. Photo by Isabelle Grégoire, L’Actualité.
What’s the potion you’re giving your man? I want the same for mine!” Claudine Uwiragiye, 27, a farmer in the Musanze district in the foothills of Volcanoes National Park in northern Rwanda, has been asked this question a hundred times. The neighbours and friends of this graceful woman in her red and yellow wrap skirt were convinced that she had bewitched her husband, so much had he changed. Previously domineering, violent and more present at the “cabaret” (local bar) than at home, 30-year-old Jean-Dedieu Manihiro, also a farmer, has become a caring spouse and father in just a few months. He is as active in raising their two children as in household chores.
“I can do anything, except breastfeed,” he says laughing as he extends his arms to his youngest daughter, who joins us in their modest house built with rammed earth on one of the “thousand hills” that have earned Rwanda its nickname. In tears, the two-year-old toddler has just stumbled into the courtyard surrounded by squash, beans and banana plantations. A hug, a few soft words in Kinyarwanda (the country’s main language) and the little girl has already forgotten her boo–boo. “He’s not the same man anymore,” says Claudine, sitting beside him on one of the wooden benches that furnish the room with its dirt floor and walls adorned with faded photos of their wedding in 2017.
“At first, when the village boys saw me peeling potatoes or cradling my baby, they laughed at me,” says Jean-Dedieu, wearing a striped polo shirt and black pants in green rubber boots. “For them, I was no longer a man.” However, little by little, they realized that the change was for the better. Not only did the family no longer have to live with banging and screaming, they had also managed to improve their income. “I no longer spend all my harvest money on alcohol, and we manage our budget together.”
However spectacular, Jean-Dedieu’s transformation has nothing to do with magic. Rather than make him drink an elixir, Claudine persuaded him to sign up with her for the Bandebereho (“role model,” in Kinyarwanda) program, a “Journey of Transformation” of 17 weekly sessions of three hours each, offered to young parents by the Rwanda Men’s Resource Centre (RWAMREC). “Otherwise, I would’ve ended up reporting him to the police.”
Based in Kigali, this NGO works to eradicate violence against women by promoting “positive masculinity.” To convince the most stubborn, male facilitators — from the targeted communities — repeatedly visit households in conflict, the list of which is provided to them by local authorities. The “role models,” like Jean-Dedieu, are encouraged to support them by becoming “agents of change” in their village.
According to the 2020 National Institute of Statistics report, 46% of married Rwandan women have suffered domestic violence, and 60% consider it acceptable. A culture of silence continues to prevail, even though the number of cases reported and examined has more than doubled in five years, topping 14,500 cases in 2021–2022.
“It’s impossible to change social norms and achieve gender equality if men aren’t involved,” says Fidèle Rutayisire, 48, executive director of RWAMREC, which he founded in 2006. A lawyer by training and a convinced feminist, he himself grew up in a violent home. “It’s easier for men to be changed by their peers than by women,” he asserts. The aim is to put an end to the myths associated with masculinity; for example, that only women can look after children, or that it’s acceptable to beat your wife if she burns a meal. But also to enable women to emancipate themselves through paid employment.
Some 50,000 men are reached each year by the Resource Centre through its various programs (including Bandebereho), deployed throughout this country of 14 million inhabitants. “It’s a drop in the bucket compared to what’s needed, but it’s essential work: too many homes are still plagued by violence,” observes Fidèle Rutayisire, with a round face and a gentle look behind his glasses. The violence was inherited from the genocide that tore Rwanda apart in 1994. In 100 days, a million Tutsis were exterminated, mostly with machetes, by the Hutu majority group. Between 250,000 and 500,000 women were raped, many of whom became pregnant (between 10,000 and 25,000 “children of hate” are thought to have been born of these rapes). Although 65% of the population is now under the age of 30 and did not experience these horrors, the trauma remains, both for the children of the genocidaires and those of the survivors.
At the end of the genocide, 70% of Rwanda’s population was made up of women who had become heads of household (widows, wives of genocidaires in prison or exile, orphans). They have therefore played a major role in the reconciliation and reconstruction of the country. As the Constitution prohibits all forms of discrimination, there are no longer any privileges linked to ethnicity (Tutsis, Hutus, Twas), religion (Christians, Muslims) or region… everyone is Rwandan. In 30 years, immense progress has been made (education, health, safety, cleanliness, etc.). And this small, green country in the Great Lakes region, landlocked between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Tanzania, Uganda and Burundi, is the only one in the world to have a majority of women in Parliament (61% of the members of parliament).
“In our post-conflict society, the only option was to bring citizens together on an equal footing,” says Liberata Gahongayire, president of Pro-Femmes/Twese Hamwe (“All together,” in Kinyarwanda), a collective involved in the process since 1994 (mobilization of women, revision of laws). However, we had to redouble our efforts. “In addition to the ethnic divisions that had torn families and society apart, patriarchal tradition relegated women to the background,” continues this historian, a researcher at the Centre de gestion des conflits de l’Université du Rwanda and the Université Libre de Bruxelles. “Many were illiterate and had never worked outside the fields.” Over the years, laws guaranteeing their rights have been passed — access to education, maternity leave, abortion (limited to critical cases), criminalization of domestic violence, the right to contraception (from age 18), and to inheritance.
Alongside the pioneering RWAMREC, many other organizations are focusing on positive masculinity. Like the Pro-Femmes organization, which includes it in its “gender equality transformation journey” for women and couples. “Positive masculinity has a dual purpose: to reduce gender-based violence and to improve the socio-economic situation of families, and therefore of the nation,” says Liberata Gahongayire.
Another major player is the British NGO Aegis Trust, designer and manager (on behalf of the Rwandan government) of the Genocide Memorial, perched on a hill in the capital, where the remains of 250,000 victims of the genocide against the Tutsis are laid to rest. Aegis Trust offers peace education programs aimed at a wide range of audiences (political decision-makers, teachers, young people, etc.), with a particular focus on positive masculinity.
“Our training courses open up dialogue in schools, at work and in the religious domain, and show the indispensable contribution of men in promoting gender equality.”
The Rwandan government encourages and supports the movement. Involving men in this promotion of equality is one of the priorities of the new gender policy, launched in 2021 by the Ministry of Gender and Family Promotion. The Ministry of Health is committed to the wider deployment of the Bandebereho program, supported by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC) in Ottawa.
The concept of positive masculinity is also spreading elsewhere in Africa. After the DRC and Senegal, South Africa hosted the African Union’s 3rd Men’s Conference on Positive Masculinity to end violence against women and girls in 2023. The African Union is encouraging civil society, religious leaders and economic players to work together. It’s a long-term project, as there is strong resistance everywhere: men fear being ridiculed and losing their power.
Considered a model of African development, Rwanda has been led since 2000 by President Paul Kagame, 66, who was re-elected on July 15 for a fourth term. A former commander in the Rwandan Patriotic Front, which stopped the genocide in 1994, he is hailed for having reconciled and modernized the country. Agriculture (coffee, tea, sorghum, etc.) still accounts for 25% of GDP and 56% of jobs. Nevertheless, the “land of a thousand hills” is enjoying annual economic growth of around 7% to 8%, thanks in particular to business and upmarket tourism. As clean as it is safe, the capital, Kigali, with its 1.7 million inhabitants, boasts grand hotels and an iconic convention centre, inspired by an old royal palace. Luxury guest houses have sprung up around national parks such as Volcanoes — where a permit for a brief visit to the mountain gorillas costs USD1,500.
Few people openly criticize Paul Kagame in Rwanda, but his detractors criticize him for his authoritarianism — widespread surveillance, non-existent press freedom, muzzling of opponents… He was recently returned to power with 99.15% of the vote. Rwandans are also subject to strict rules intended to strengthen national unity. For example, all pupils in the public sector, boys and girls alike, must have their heads shaved for reasons of hygiene and equality. And every last Saturday of the month, citizens are required to take part in umuganda (community work), or face a fine.
Nevertheless, inequalities remain. The second most densely populated country in Africa (after Mauritius), Rwanda ranks 161st (out of 193) on the UN Human Development Index, which measures health, education and the standard of living to determine the degree of “development.” And despite the fact that women make up a majority in Parliament, the patriarchy is still alive and well. Boys still grow up with the idea that they are superior to girls, and sexist violence persists.
“The woman is the heart of the home, the man is the master of the family,” according to a Rwandan saying. Roles are still firmly entrenched, especially in rural areas where 83% of the population lives. Submissive and self-effacing, the abagore (women) work in the fields with their babies strapped to their backs, walk for miles to fetch water, and do most of the unpaid work. The abagabo (men) are the breadwinners, they make all the decisions for the family, feel that sex is their right, and enjoy their free time as they please.
These differences become apparent during the Bandebereho workshops. On the day of my visit, some 30 men and women are sitting in a circle in a room at the health centre in Gitare, Northern Province. Most came on foot along a red laterite track, with the bluish peaks of the volcanoes marking the border with Uganda in the background. After the dances, songs and motivational slogans that precede each session, five male volunteers leave while the facilitator sets up the equipment for a role-play of domestic chores: cloth doll, laundry tub, broom, water pot and container.
Back in the room, each man mimes a task — rocking the baby, sweeping the yard, preparing dinner… — before leaving the stage, relinquishing his responsibility to the remaining men. In the end, only one is left to do it all, not knowing what to focus on. “And he doesn’t even have any dishes to wash!” exclaims one participant, to general hilarity. “It was super-stressful!” admits the visibly disoriented volunteer. “I suddenly realized how much my wife does at home: she never rests!”
(Article continued in right column)
(click here for the article in French.)
Question related to this article:
Protecting women and girls against violence, Is progress being made?
What role should men play to stop violence against women?
(Article continued from left column)
In addition to role-playing and homework, participants in Bandeberehosessions are expected to contribute to group discussions. And reflect on their behaviour, which is often identical to that of their fathers. “The men learn to talk about their private lives and open up about their emotions, something they’re not used to doing,” says Emmanuel Karamage, a sturdy 50-year-old who coordinates the initiative for the Musanze district. “Then, they communicate better with their spouses at home.”
At a session I attended, the local leader launched a debate on sexual consent. “Before RWAMREC, there was no such thing as consent: my husband would come home drunk from the cabaret and throw himself at me without even saying hello,” says a 30-something mother of four. “If I didn’t give in, he’d hit me.” There are embarrassed murmurs from the men in the audience: they too used to act like this, but swear they’ve changed. “We’ve even introduced foreplay!” says one of them, grinning from ear to ear.
The practical exercises are also revolutionary. Like carrying a baby on your back, an ancestral technique handed down from mother to daughter. “Our fathers never did this, and nobody taught us how to do it,” says Jean-Baptiste Singiranumwe, a 31-year-old farmer. A father of two, he completed his transformation in 2022. He welcomes me to the family home in Kamugeni, in the North — an ochre house, flanked by a chicken coop and lined with pious inscriptions. Jean-Baptiste is quick to show me how he places his youngest child, delighted, on his back with the help of a wrapper, under the tender gaze of his wife, Claudine Nyiramunezero. With steady movements that he rehearsed many times in class with a doll, he beams with pride. “I feel super-connected to my child.”
A brutal ex-alcoholic, Jean-Baptiste nevertheless made life hell for his wife, who later confided in me that she’d thought of leaving him and even killing him. He was eventually sentenced to two years of prison, after violent fights in the village. Upon his release, the local RWAMREC animator, a neighbour who knew him well, came to talk to him about Bandebereho. As in the case of Jean-Dedieu and the dozens of men initiated into positive masculinity that I met during this reporting assignment, his transformation was radical. At least, that’s what they say, with the approval of their wives, even when I talk to them alone.
From the outside, this may seem inconceivable. How can such macho men change so completely in such a short time? According to Fidèle Rutayisire, founder of RWAMREC, various factors come into play, including the training style (participative), the proximity of the trainers and the unconditional support of local leaders.
A local councillor and a policeman were also present at a BAHO (Building and Strengthening Healthy Households) workshop, another RWAMREC program, which I attended in Gatsibo, Eastern Province. Both spoke to encourage the participants. “RWAMREC is helping us to stabilize security in the region,” said the policeman, standing straight in his black boots. “Peace at home is the first pillar of our country’s development.”
To better understand the real impact of positive masculinity programs in Africa, a major study was conducted by the Washington-based International Center for Research on Women (ICRW), with financial support from IDRC in Ottawa. Published in 2023, this study (“Promoting positive masculinity for sexual and reproductive health and rights and gender equality in informal settlements in sub-Saharan Africa”) covered three countries (DRC, Rwanda and Nigeria) and compared the attitudes and perceptions of men who had or had not participated in these programs (1,500 interviewees).
First observation: being made aware of positive masculinity doesn’t necessarily lead to a positive change in behaviour. “Many NGOs offering these programs lack sufficiently skilled staff and the financial resources to ensure the assessment and follow-up necessary,” observes Chimaraoke Izugbara, director, Global Health, Youth & Development at ICRW. The programs examined varied in quality, both in terms of duration (from a simple one-hour presentation to a more elaborate training course) and content. “They focus on harmony in couples, but don’t always encourage men to critically self-reflect on gender norms,” continues the Nigerian-born researcher, reached at his Washington office. “What’s more, they are often implemented without considering the country’s socio-economic and cultural context.”
Collaborating on this study in Rwanda, researcher Ilaria Buscaglia interviewed participants in the Bandebereho program, which is doing well. “The men who follow this path evolve significantly, they don’t justify any form of gender-based violence, drink less and participate more in domestic tasks,” observes this Italian anthropologist, who has been based in Rwanda since 2013, where she has worked for various NGOs, including the Men’s Resource Centre. “But more needs to be done to change gender norms: at the moment, men ‘help’ their wives and welcome the improved household income, but they consider themselves to be the heads of the family.”
The study by the Washington-based International Center for Research on Women also highlights the fact that certain themes associated with positive masculinity have a hard time breaking through, even among respondents who have attended these programs. For example, most of them have never been tested for HIV/AIDS. The same rejection applies to sexual diversity. “Homophobia is still very present, and none of these programs mention it,” says Ilaria Buscaglia. The subject is taboo (for religious and other reasons) in the three countries studied, including Rwanda, even though homosexuality is not criminalized on Rwandan soil — unlike in many African countries. “The mere mention of LGBTQ+ rights can derail all our efforts on gender equality.”
There is still a lot of work to be done to change mentalities. The large-scale deployment of the Bandebereho program, which started in 2023, could contribute to this. Previously extended to 30,000 couples, this time it aims to reach 84,000 families in the Northern Province by 2027. Carried out by the Ministry of Health and the Rwanda Biomedical Centre in partnership with RWAMREC, this initiative is co-funded by Global Affairs Canada and IDRC ($1.2 million), and has also received support from Grand Challenges Canada ($1 million) and the Global Innovation Fund ($2.5 million).
To better reach families, the Ministry of Health relies on the network of community health workers (CHWs), volunteers who fill the gaps left by a shortage of medical staff throughout Rwanda. Some 1,600 CHWs (out of the country’s 60,000), trained by RWAMREC, recruit couples and offer the 17 Bandebereho sessions in their communities. The program will be monitored throughout the process. In the long term, the initiative, integrated into the health system, could be extended to all 30 of the country’s districts.
Inspired partly by the Rwandan experience, positive masculinity programs are proliferating in sub-Saharan Africa, especially in poor urban areas, where the need is great. As the ICRW study points out, a growing number of Africans are forced to live in slums, where gender-based violence, unwanted pregnancies and unsafe sexual practices are exploding. In addition, as in Nigeria and the DRC, years of armed conflict, insecurity and violence have increased toxic masculinity and the lack of services for sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Ivorian sociologist Ghislain Coulibaly, 45, father of three, is one of the continent’s most ardent advocates of positive masculinity. A former technical advisor to Côte d’Ivoire’s Ministry of Women, Family and Children, and an excellent communicator, he is the author of a TEDx conference on the subject, broadcast on YouTube. This earned him mockery and threats on social media. “Why do you want to reverse the social order?”
“A minority of Ivorian men are really aware of what’s at stake,” says the sociologist from his home in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire. “Many believe that I’m dismantling their power to give it to women, and that positive masculinity perverts the values of Ivorian society.” He’s also a target for some women, who feel he takes up too much space and should let them fight their own battles.
This does not discourage him. “These criticisms are part of the societal evolution.” In 2019, Ghislain Coulibaly created the Réseau des hommes engagés pour l’égalité de genre (RHEEG) in Côte d’Ivoire. A network that has already inspired others: in the DRC in 2022 and in Cameroon this year. RHEEGs offer, among other things, activities to raise awareness among the police and military (DRC) and in elementary schools (Côte d’Ivoire).
He believes there is hope. “With the advent of digital technology and social networks, young people are much more open to other cultures and ways of doing things,” he says. “There is also an increasing number of young girls going to school.” This should rebalance male–female power dynamics. “Education is the driving force behind this transformation.”
This is also the aim of the Rwandan feminist NGO Paper Crown, which works with 14-to-19-year-olds. Its flagship program, My Voice, My Power (a four-hour weekly workshop lasting 18 weeks), aims to change young people’s minds about gender norms, and to turn them into leaders capable of influencing their peers and parents alike.
On this Saturday morning in April, about 50 registered teenagers have come to the Kayonza youth centre in the Eastern Province, a two-hour drive from Kigali, where they are conducting the training. It’s hard to tell the boys from the girls: they all wear their hair cropped, in loose-fitting T-shirts and sports shorts. After a snack of doughnuts provided by the NGO, the girls stay in the breezy room, while the boys head to a tent set up a few yards away on a grassy field.
“Before mixing the groups, we start by making it clear to the girls that social barriers limit their development, but that they have rights,” explains Clementine Nyirarukundo. Long braids, jeans and sneakers, the manager of programs and partnerships at the NGO conducts the workshop with the teenagers. “This helps them gain self-confidence.” Most of those present are still intimidated and tend to speak softly, with their gaze downcast. A visit from a Canadian journalist doesn’t help matters. But Clementine quickly puts them at ease. Today’s lesson focuses on a new method for resisting assaults (defining boundaries, de-escalation, physical self-defence tactics…). Little by little, the girls get bolder and share their experiences. Clementine insists on the importance of asserting yourself, looking up and making eye-contact when speaking.
In the tent, the boys also work on themselves. They draw self-portraits and write on each body part what affected them as children: their fears, their aspirations, their good and bad habits related to gender (entering a girl’s room without her permission, giving her a bad reputation, fighting…). “Be honest, don’t embellish anything!” says Théophile Zigirumugabe, their trainer. Jovial and eloquent, he captures their attention by using their language, foul language included. The practical exercises — aimed at both boys and girls — also include putting a condom on a banana. Earlier this morning, period products were the focus. Without any embarrassment, a slim 15-year-old presented a sanitary napkin to his group, unfolded it and placed it carefully on a pair of underwear brought by the trainers. “It eliminates the shame associated with periods,” says Clementine. “We want to show that it’s normal and that it’s part of daily life.”
There are loud shouts from the girls’ workshop at the other end of the field: “No! No! No!” The boys barely look up from their drawings. They know what’s happening. Divided into two rows facing each other, the girls practise saying “no!” to an assailant while waving a hand in front of them. “The aim is to use the voice rather than force,” says Clementine Nyirarukundo. “Everyone needs to understand that it’s a weapon.” A weapon far more powerful than any magic potion.
Isabelle Grégoire visited Rwanda at the invitation of the International Development Research Centre.
This article was originally published in the November 2024 issue of L’actualité, under the title “L’arme de paix de la masculinité positive”
– – – – – –
If you wish to make a comment on this article, you may write to coordinator@cpnn-world.org with the title “Comment on (name of article)” and we will put your comment on line. Because of the flood of spam, we have discontinued the direct application of comments.










