.. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT ..
An article by Emilio Godoy for the Inter Press Service (reprinted by permission)
Achuar indigenous communities in Ecuador are turning to the sun to generate electricity for their homes and transport themselves in canoes with solar panels along the rivers of their territory in the Amazon rainforest, just one illustration of how indigenous people are seeking clean energies as a partner for sustainable development.
“We want to generate a community economy based on sustainability,” Domingo Peas, an Achuar leader, told IPS. Peas is also an advisor to the Confederation of Indigenous Nationalities of the Ecuadorian Amazon, which groups 28 indigenous organisations and 11 native groups from that South American country.

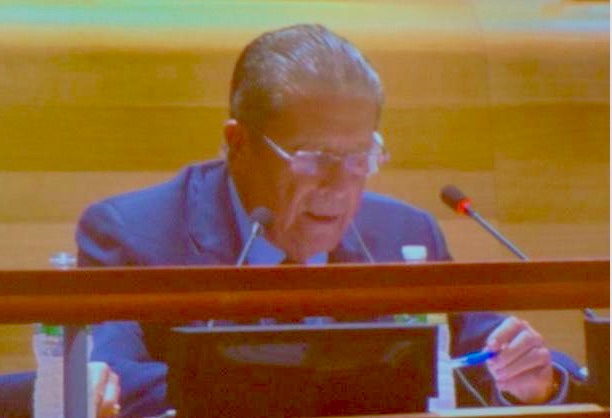
United Nations Special Rapporteur on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, Victoria Tauli-Corpuz of the Philippines (3rd left), calls for the full participation of indigenous communities in clean energy projects during the forum Our Village in San Francisco, California. Credit: Emilio Godoy/IPS
The first project dates back to the last decade, when the Achuar people began to install solar panels in Sharamentsa, a village of 120 people located on the banks of the Pastaza River. Currently they are operating 40 photovoltaic panels, at a cost of 300 dollars per unit, contributed by private donations and foundations.
The villagers use electricity to light up their homes and pump water to a 6,000-litre tank.
“There is a better quality of services for families. Our goal is to create another energy model that is respectful of our people and our territories,” Peas said.
The Achuar took the next step in 2012, when they started the Kara Solar electric canoe motor project. Kara means “dream” in the Achuar language.
The first boat with solar panels on its roof, with a capacity to carry 20 people and built at a cost of 50,000 dollars, began operating in 2017 and is based in the Achuar community of Kapawi.
The second canoe, with a cost of 35,000 dollars, based in Sharamentsa – which means “the place of scarlet macaws” in Achuar – began ferrying people in July.
The investment came partly from private donations and the rest from the IDEAS prize for Energy Innovation, established by the Inter-American Development Bank, which the community received in 2015, endowed with 127,000 dollars.
The Achuar people’s solar-powered transport network connects nine of their communities along 67 km of the Pastaza river – which forms part of the border between Ecuador and Peru – and the Capahuari river. The approximately 21,000 members of the Achuar community live along the banks of these two rivers.
“It was an indigenous idea adapted to the manufacture of canoes. They use them to transport people and products, like peanuts, cinnamon, yucca and plantains (cooking bananas),” in an area where rivers are the highways connecting their settlements, said Peas.
The demand for clean energy in indigenous and local communities and success stories such as the Achuar’s were presented during the Global Climate Action Summit, convened by the government of the U.S. state of California.
The event, held on Sept. 13-14 in San Francisco, was an early celebration of the third anniversary of the historic Paris Agreement on climate change, reached in the French capital in December 2015.
Native delegates also participated in the alternative forum “Our Village: Climate Action by the People,” on Sept. 11-14, presented by the U.S. non-governmental organisations If Not US Then Who and Hip Hop Caucus.
In addition to Ecuador, innovative experiences have also emerged from indigenous communities in countries such as Australia, Bolivia, Canada, Guatemala, Malaysia, Nicaragua, the Philippines, and the United States, according to the forum.
(Continued in right column)
Question for this article:
Are we making progress in renewable energy?
Indigenous peoples, Are they the true guardians of nature?
(Continued from left column)
For example, in Bolivia there is an alliance between the local government of Yocalla, in the southern department of Potosí, and the non-governmental organisation Luces Nuevas aimed at providing electricity from renewable sources to poor families.
In Yocalla, a municipality of 10,000 people, mainly members of the Pukina indigenous community, “755 families live in rural areas with limited electricity; the national power grid has not yet reached those places,” project consultant Yara Montenegro told IPS.
Thanks to the programme, which began in March, 30 poor families have received solar panels connected to lithium batteries, produced at the La Palca pilot plant in Potosí, which store the fluid.
Each system costs 400 dollars, of which the families contribute half and the organisation and the government the other half. The families can connect two lamps, charge a cell phone and listen to the radio, replacing the use of firewood, candles and conventional batteries.
The development of clean sources plays a decisive role in achieving one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which make up the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Goal seven aims to establish “affordable and non-polluting energy” – a goal that also has an impact on the achievement of at least another 11 SDGs, which the international community set for itself in 2015 for the next 15 years, within the framework of the United Nations.
In addition, the success of the Sustainable Energy for All Initiative (SE4All), the programme to be implemented during the Decade of Sustainable Energy for All 2014-2024, which aims to guarantee universal access to modern energy services, and to double the global rate of energy efficiency upgrades and the share of renewables in the global energy mix, depends on that progress.
But most of the groups promoting an energy transition do not include native people, points out the May report “Renewable Energy and Indigenous Peoples. Background Paper to the Right Energy Partnership,” prepared by the Indigenous Peoples’ Major Group for Sustainable Development (IPMG).
That group launched a Right Energy Partnership in July, which seeks to fill that gap.
For Victoria Tauli-Corpuz of the Kankanaey Igorot people, who is the U.N. Special Rapporteur on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, energy represents “a problem and a solution” for indigenous people, she told IPS at the alternative forum in San Francisco.
“The leaders have fought against hydroelectric dams and I have also seen projects in the hands of indigenous peoples,” she said.
Because of this, “the communities have to be at the centre to decide on and design projects that help combat poverty, because they allow electricity without depending on the power grid, and they strengthen the defense of the territory and benefit the people,” she said.
“It’s about guaranteeing rights and defining development processes,” she summed up.
Examples of projects that can be replicated and expanded, as called for by the U.N special rapporteur, are provided by communities such as Sharamentsa in Ecuador and Yocalla in Bolivia.
Sharamentsa operates a 12 kW battery bank that can create a microgrid. “A power supply centre is planned that allows the generation of value-added products, such as plant processing,” Peas said.
In Yocalla, the plan is to equip some 169 families with systems in December and then try to extend it to all of Potosí. But Montenegro pointed out that alliances are needed so that the beneficiaries can pay less. “In 2019 we will analyse the impact, if the families are satisfied with it, if they are comfortable,” she said.
This article was produced with support from the Climate and Land Use Alliance.
(Thank you to Janet Hudgins, the CPNN reporter for this article.)