TOLERANCE & SOLIDARITY .
An open letter published by Pressenza (reprinted under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license)
His Excellency Mr. Antonio Guterres Secretary-General United Nations Headquarters, New York City
Dear Mr. Secretary-General,
We are writing to you as International Fellowship of Reconciliation, a global movement seeking to transform, through nonviolence, the world away from endless cycles of violence towards justice, reconciliation, and lasting peace. As a concerned international NGO, accredited to the UN ECOSOC, we are writing to you to express our appreciation for your efforts dealing with the current health crisis in the world and to share some of our thoughts with you at this difficult time.

We join with you in recognizing “the fury of [COVID-19] illustrates the folly of war,” and we thank you for your leadership in calling for a global ceasefire as a first step to “end the sickness of war”. We are encouraged that your call has resonated with millions across the world, and gained endorsements from 70 Member States, with expressions of acceptance from parties to conflict, and non-state actors as well.
We call on all UN member States to support Your appeal, to the General Assembly and to the Security Council, and put it into practice.
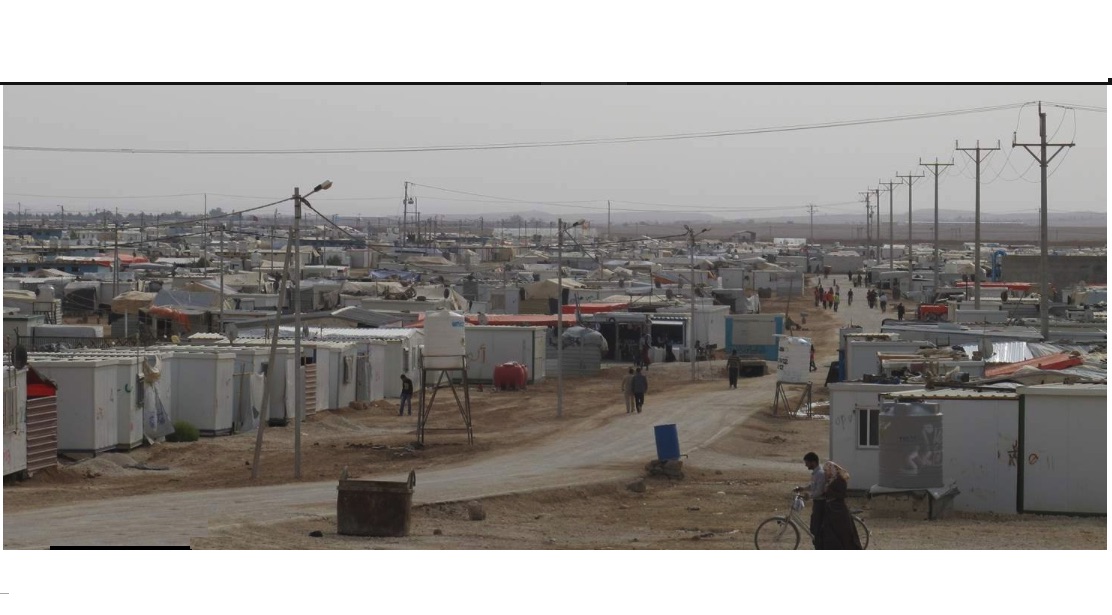
The pandemic has revealed the single common vulnerability of humankind, which knows no border. We who are but one of the species on the planet earth must shun our urge for identity superiority or risk even more devastating pandemics. With this shattered illusion of separateness, humanity cannot tolerate war and violence anywhere, as it threatens health and peace for everyone everywhere. Countries are grappling internally with political, economic, racial, and social divides that exacerbate efforts to contain the virus, while inequity in the global community reveals the new depths of suffering in countries that already bear the brunt of the pain caused by climate change, hunger, economic sanctions and exploitation, and armed conflicts.
While the impact of COVID-19 on the countries where we have active members has varied, together, we affirm the urgency for a new and creative way forward that builds human security globally through health, economic justice and peace. We therefore appeal:
(continued in right column)
How can we work together to overcome this medical and economic crisis?
(continued from left column).
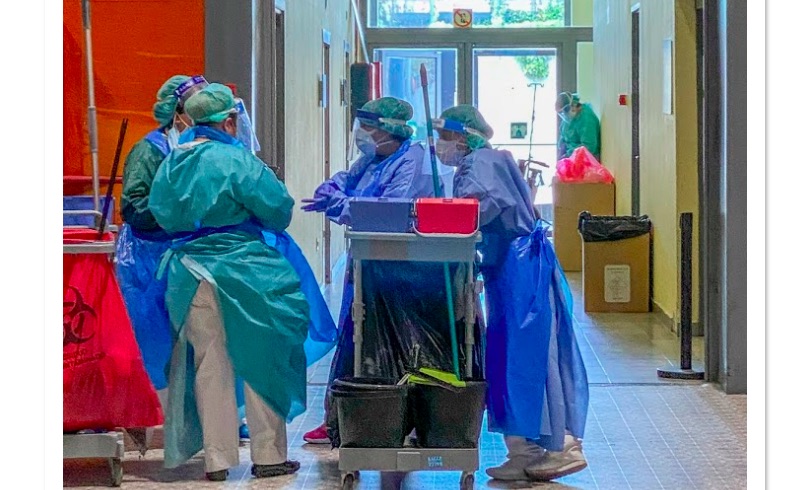
1. Prioritize the protection of poor and marginalized people. Economic inequality increases the impact of the pandemic and sets the stage for more devastation with the risk of even greater lethality. For instance, underinvestment in healthcare means many countries are unable to meet the simple challenge of providing personal protective equipment to those in need. Concentrated poverty means sheltering in isolation, and for women and children locked down with abusers, it promises new levels of violence, abuse, and death.
2. Protect civil liberties and human rights. Emergency legislation rushed through in many coun- tries may serve as cover for oppressive measures and the violation of human rights. Traditionally marginalized communities are forgotten or ignored, and vulnerable people are cut off from offi- cial support. We urge you, Mr. Secretary-General, to prioritize and support the work of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights Ms. Michelle Bachelet to adapt the global index for hu- man rights to ensure that it monitors abuses in a world now reshaped by COVID-19 legislation. We urge you to call on all member States for accountability.
3. Use the momentum of this global crisis to shift resources to meet human needs and create lasting peace. Weapons of war cannot defeat a virus, address climate change, nor solve any other world problem. As States pursue ‘business as usual’ military strategies to contain the virus and create security, the world wastes opportunities to coalesce around creative responses that match the grave nature of this crisis, like protecting the most vulnerable from harsh economic impacts and working in solidarity to ensure global health emergency preparedness. These are the kinds of creative responses that lead to lasting peace. We call for disarmament and a major reduction in military spending worldwide, starting with the abolition of all nuclear weapons. We call for the conversion of military industry to civilian production and for the end of exports of weapons to states at war or violating human rights. Humanity will thrive with equitable local community investment and the shift from funding warfare to funding healthcare and peace. We urge the United Nations to invest more capacity and financial support in nonviolent conflict transfor- mation, mediation and Unarmed Civilian Peacekeeping.
Now is the time to create a “new normal” built on a culture of peace and non-violence. We call for global bridge-building and cooperation, and global leadership encouraging increased global solidarity. The 2030 Sustainable Development Goals recognize the interconnected reality of our world. With branches, groups, and affiliates in more than 40 countries, IFOR offers its support to UN agencies in achieving these goals. By highlighting the centrality of peace to a world free from poverty and ine- qualities, the SDGs challenge the world to put into practice a new way of thinking. Addressing the issues named above ensures that nations can create roadmaps out of COVID-19 that leave no one behind.
We wish you well and further success in your work.
Charlotte Sjöström Becker, President of the International Fellowship of Reconciliation
[Editor’s note: The International Fellowship of Reconciliation (IFOR) was founded in 1914 in response to the horrors of war in Europe. Today IFOR counts 71 branches, groups and affiliates in 48 countries on all continents.]