. . SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT . .
An article from the International Institute for Peace Tourism
The IIPT Global Peace Parks Project was launched this past week with the dedication of Pu’er Sun River National Park as an IIPT International Peace Park in collaboration with the China Chamber of Tourism. Dignitaries participating in the ceremony included Madame Wang Ping, Founding Chairman, China Chamber of Tourism (Photo on the left); Mr. Peter Wong Man Kong, Executive Chairman, China Chamber of Tourism; Mr. Yu Jinfang,Co-founder and Developer of Pu’er Sun River National Park; Mrs. May Jinfang, Co-founder and Developer; Mr. Carlos Vogeler, Executive Director, UN World Tourism Organization; Mr. Xu Jing, Regional Director for Asia and Pacific, UN World Tourism Organization; Hon. Gede Ardika, former Minister, Culture and Tourism, Indonesia; Helen Marano, Government and Industry Affairs Director, World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC); Louis D’Amore, IIPT Founder and President and various city officials of Pu’er City.
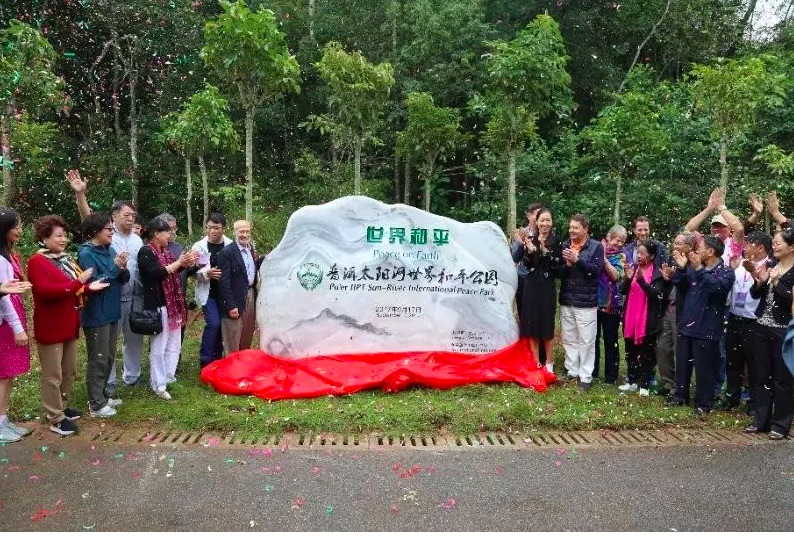

Members of China Chamber of Tourism following the unveiling of the stone plaque
click on photo to enlarge
China Chamber of Tourism Chairman, Peter Wong stated: “Pu’er Sun River National Park is the perfect site for the first IIPT International Peace Park in China as it is a national model of the “wild beauty of nature” covering an area of 216 square kilometers with a wide variety of plants and 812 species of wildlife. In is also a model of people in harmony with nature showcasing the local culture of the diverse ethnic people of the region.”
In his Peace Park dedication address, IIPT Founder and President Louis D’Amore said: “It is truly an honor to be here with you today as we dedicate this IIPT International Peace Park – the first in China, just a few days before the UN International Day of Peace, September 21 – and in support of UN Sustainable Development Goal 16 which calls for peaceful – inclusive and just societies. As we dedicate this park, we also begin what I am sure will be an important and fruitful relationship between the China Chamber of Tourism and the International Institute for Peace through Tourism; a relationship that will bring more peace parks in China and contribute towards the vision of tourism becoming the world’s first global peace industry – and the belief that every traveler is potentially an ambassador for peace.”
The Pu’er Sun River National Park focuses on the theme “wild beauty of nature” in combination with the local culture and the harmony of humans with nature. By operating profit-making projects within the Park, it is able to effectively provide sustainable protection for precious and unique natural and cultural resources. The Pu’er Sun River National Park also serves as a Forest Ecological System Science Education Base; Flora and Fauna Rescue Base; and Global Tourist Attraction for visitors to experience nature and the Pu’er Culture.
(continued in right column)
How can tourism promote a culture of peace?
(continued from left column)
The IIPT Global Peace Parks project has a goal of 2,000 Peace Parks circling the earth by 11 November 2018 – the 100th Anniversary of the end of World War I. The four year commemoration of the World War I Centenary, with its theme of “No More War” – has been supported by IIPT since its launch in 2014.
IIPT is proud to have United Cities and Local Governments (UCLG) as a partner in its global campaign. UCLG is the united voice and world advocate of democratic local self-government with a global network of cities, local and regional governments representing 70% of the world population. UCLG goals include contributing to the achievement of the SDG’s, Paris Agreement, Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, and New Urban Agenda for Sustainable Urban Development.
The Global Peace Parks Project builds on the success of IIPT’s 1992 “Peace Parks across Canada” Project commemorating Canada’s 125th birthday as a nation. IIPT conceived and implemented “Peace Parks across Canada” which resulted in 350 Peace Parks being dedicated by cities and towns from St. John’s, Newfoundland on the shores of the Atlantic, across five time zones to Victoria, British Colombia on the shores of the Pacific.
The Peace Parks were all dedicated on October 8, 1992 as a National Peace Keeping Monument was being unveiled in Ottawa and 5,000 Peacekeepers passing in review. Each park was dedicated with a ‘bosco sacro’ – a peace grove of 12 trees, symbolic of Canada’s 10 Provinces and 2 Territories, as a link to one another, and a symbol of hope for the future. Of the more than 25,000 Canada 125 Projects, Peace Parks across Canada was said to be the most significant.
IIPT International Peace Parks have since been dedicated as a legacy of each IIPT International Conferences and Global Summits. Notable IIPT International Peace Parks include Bethany Beyond the Jordan, site of Christ’s baptism as a legacy of the Amman Summit, 2000; Victoria Falls, as a legacy of the IIPT 5th African Conference, 2011, subsequently re-dedicated as the featured event on Opening Day of the UNWTO 20th General Assembly 2013, co-hosted by Zambia and Zimbabwe; and Medellin, Colombia, dedicated on Opening Day of the UNWTO 21st General Assembly. Photo is Dr. Kenneth Kaunda, first President of Zambia and UNWTO Secretary General, Dr. Taleb Rifai, planting the first of six olive trees during the re-dedication of the IIPT International Peace Park, Opening Day of the UNWTO 20th General Assembly.
About China Chamber of Tourism
The China Chamber of Tourism was formed in 2002 to include all sectors of the travel and tourism industry and related industries throughout China. It is based on a concept of “Pan Tourism” with the belief that tourism as a bond could connect and lead industries to develop co-operatively. Its core beliefs are “tourism is peace” and that world tourism calls for world peace; tourism is culture and the improvement of life quality. China Chamber of Tourism has achieved fruitful co-operation with UNWTO, WTTC, PATA – and now IIPT – enhancing the co-operation and exchange of Chinese and tourism enterprises of other nation